Thinking about a data governance model for deploying Power BI in an organization can be quite complex. You need to take into account a lot of key considerations and planning to make this a successful project for your enterprise.
The Power BI ecosystem is diverse and can be implemented in many different ways. A lot of usage scenarios are possible to deploy Power BI. There is no one-scenario-fits-all, but it’s a good exercise to think about a main scenario that’s generally the best approach within your company.
In fact there are 3 main categories which determine how Power BI content, like datasets and reports, are managed. Most important is to determine which implementation scenario or strategy best fits with your company specific reporting needs.
A brief summary of the differences between those 3 implementation scenarios:
| Business driven self service BI | Managed self service BI | Corporate BI | |
| Type approach | Bottum-Up | Hybrid | Top-Down |
| Description | Emphasis on data exploration and freedom | A “managed” approach where reports use predefined datasets/models | IT is responsible for report build and publication |
| Governed by | Business | IT: data & datamodels (semantic layer) Business: report | IT |
A common mistake is to automatically choose a corporate BI approach for large organizations. However the chosen approach doesn’t depend on the size of the organization but rather on the requirements of the project.
Indeed noticeably a lot of large companies go for a corporate BI approach, but that doesn’t mean they don’t need self service BI.
There are some general key aspects worth mentioning before implementing a managed self service Power BI strategy.
A Power BI shared dataset is reused among many different reports. This decentralized approach facilitates delegating report development to business users via the usage of centralized (managed) data. These datasets are published to a dedicated Power BI workspace often called a Data Hub.
Report creators can connect to the data hub and start building reports on the datasets they have granted permissions to.
One of the main advantages is the ability this creates for dataset authors and report creators to work independently from each other. A dataset author can be a IT or BI expert whereas creating reports can be delegated to business users.
These centralized datasets should be user-friendly and serve as a semantic layer. It also reduces the amount of duplicative copies of datasets.
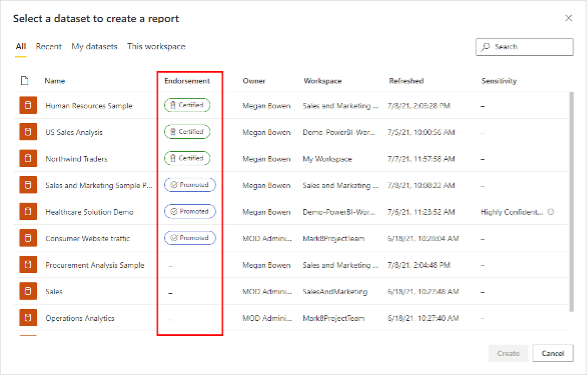
The data hub is the central location where report creators can find the datasets that are used within the organization (see image in the previous section). This contributes the reusage of datasets.
It’s the Power BI Administrator who needs to enable dataset discovery to make this possible.
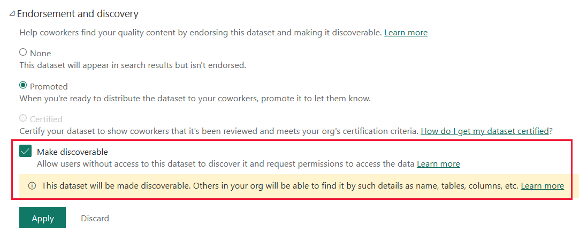
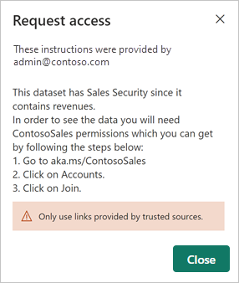
A report creator can find datasets in the data hub, but this doesn’t automatically mean he can build a report on this data. Therefore he need to request access Build permissions by adding a message via the dialog box. This action will send an email to the dataset owner.
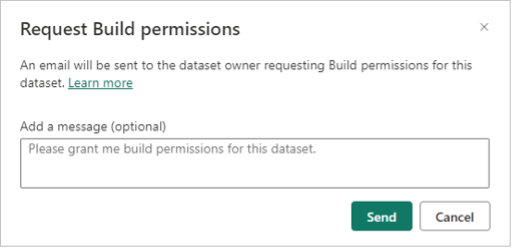
Be aware that this behavior needs to be enabled by the Power BI Administrator. Additionally he can define the request to include some instructions for the requestor.
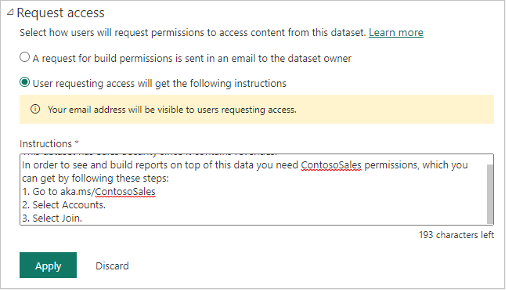
The requestor receives the following message in this case:
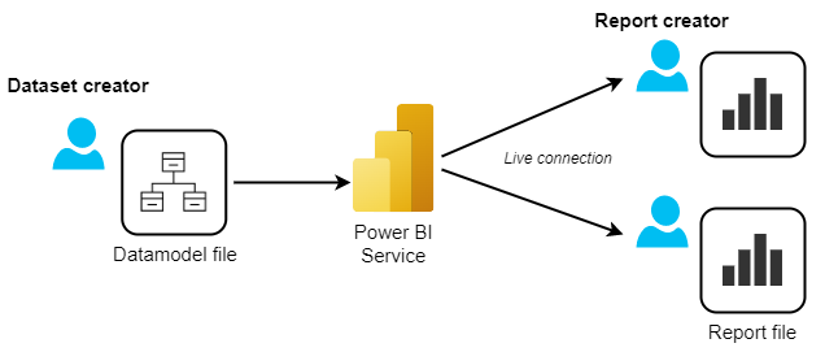
A live connection connects one or more reports to an existing dataset. This avoids the need to create a new data model for each report that’s created in Power BI Desktop.
Working with separate dataset and reporting workspaces has many advantages. Mainly it creates clarity on who is responsible for managing content in each workspace.
As a result report creators only have permissions to publish content to a reporting workspace (when at least having acontributor role). Additionally they should have permissions to specific datasets.
Within a managed self service usage scenario, there are different roles required. There should be at least one team member be assigned to each role, but it’s also possible one person taking on multiple roles. This all depends on your organization.
Now you understand important key aspects and roles for implementing managed self service BI, we can bring this all together to visualize a high level workflow for this usage scenario.
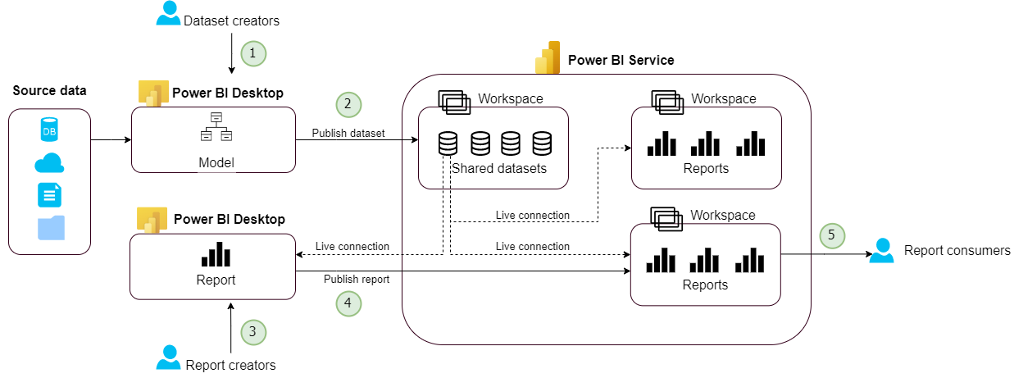
Report consumer are given workspace level permissions to view reports inside the reporting workspace.
Managed Self-Service BI (SSBI) with Power BI is an approach that empowers business users to create their own reports and dashboards while maintaining governance and control over data and its quality. It combines the flexibility of self-service BI with the oversight and support of IT.
The benefits include enhanced data accessibility, faster insights, reduced IT bottlenecks, improved data governance, and the ability for users to tailor reports to their specific needs while ensuring data integrity and security.
Managed SSBI ensures data governance by implementing data policies, monitoring data usage, and maintaining a single source of truth. IT departments can oversee data access and quality while enabling users to work independently.
Organizations can implement Managed SSBI by setting up a robust data governance framework, providing training and support to business users, leveraging Power BI’s features like dataflows and shared datasets, and continuously monitoring and optimizing the BI environment.
Still have questions about how Cloubis
can help your business with data?